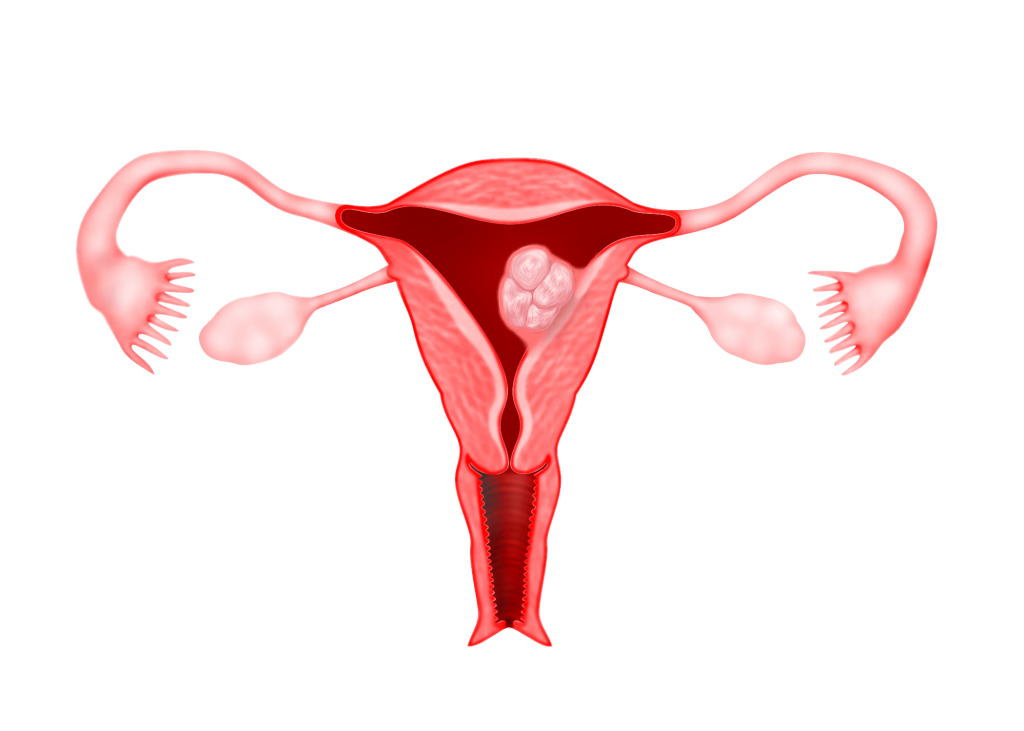
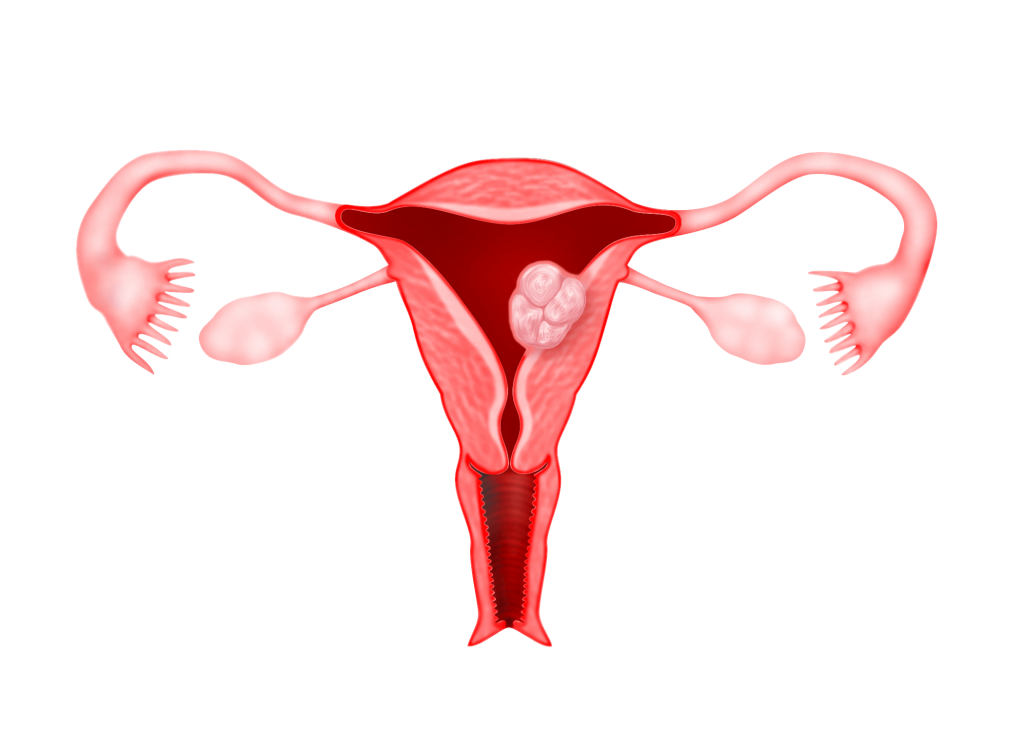
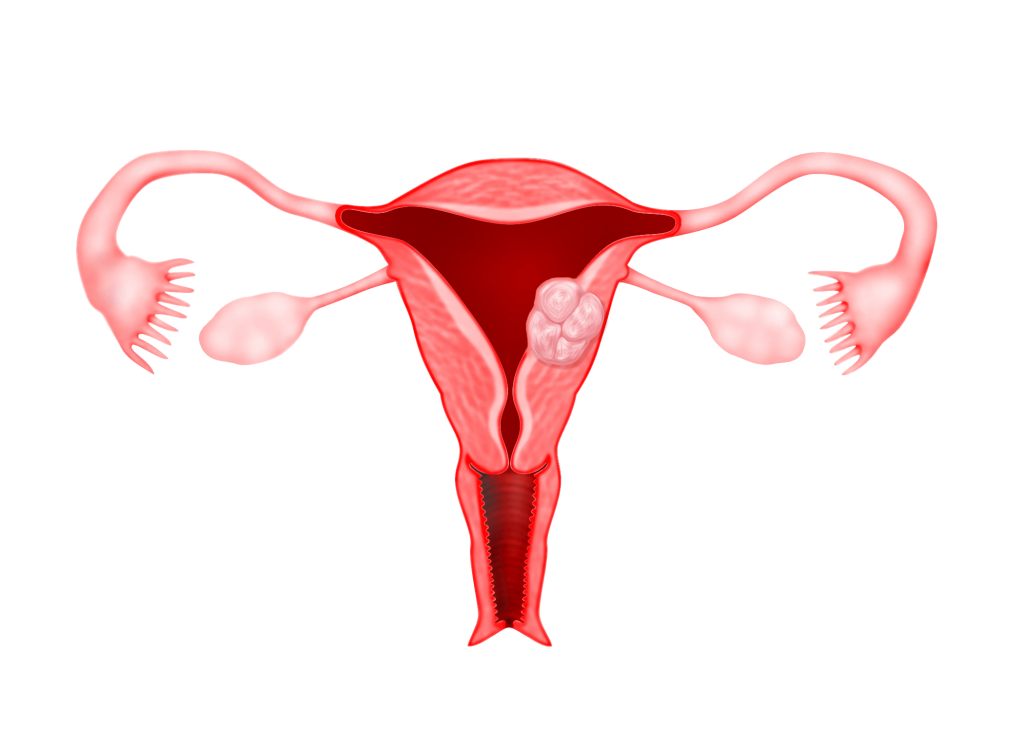
Submucous fibroids are fibroids that protrude into the uterine cavity.
These fibroids are basically divided into 3 types :
Type 0 : The fibroid is completely found in the uterine cavity with no extension into the myometrium
Type 1 : Submucous fibroid with less than 50% found within the myometrium
Type 2 : Submucous fibroid with more than 50% found within the myometrium
Symptoms
Even a small submucous fibroid can cause symptoms such as
1) heavy menses
2) prolonged menses and spotting
3) vaginal discharge
4) cramping during menses
5) bleeding after menstruation
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a submucous fibroid can be made by:
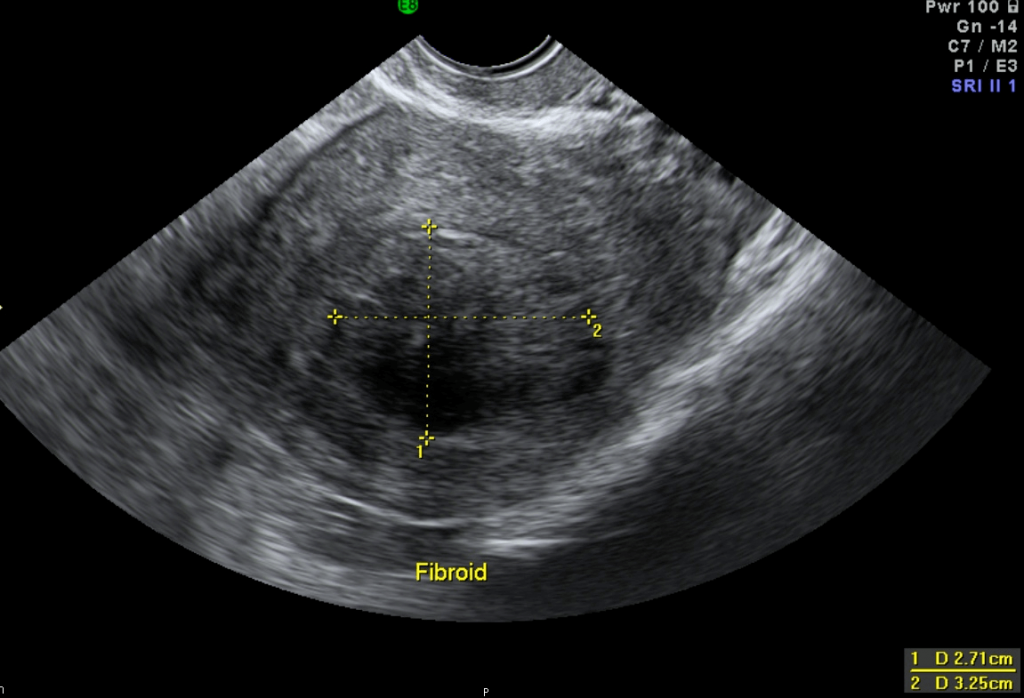
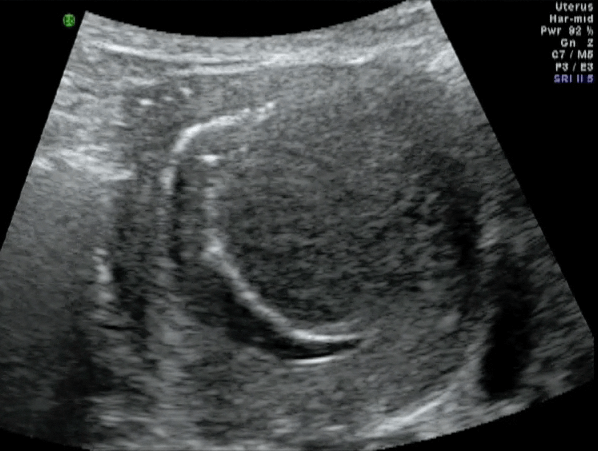
1) Transvaginal ultrasound (Figure 41.4).
2) Saline Infusion Sonology (SIS) – Fluid is injected into the uterine cavity and an ultrasound is performed. The fluid in the uterine cavity will move around the fibroid and the attachment of the fibroid to the uterus will be easily seen (Figure 41.6).
3) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – MRI can show a submucous fibroid well but this is an expensive diagnostic test
4) Office Hysteroscopy – An Office Hysteroscopy can be done to confirm the diagnosis of a submucous fibroid before surgery is contemplated (Figure 41.5).
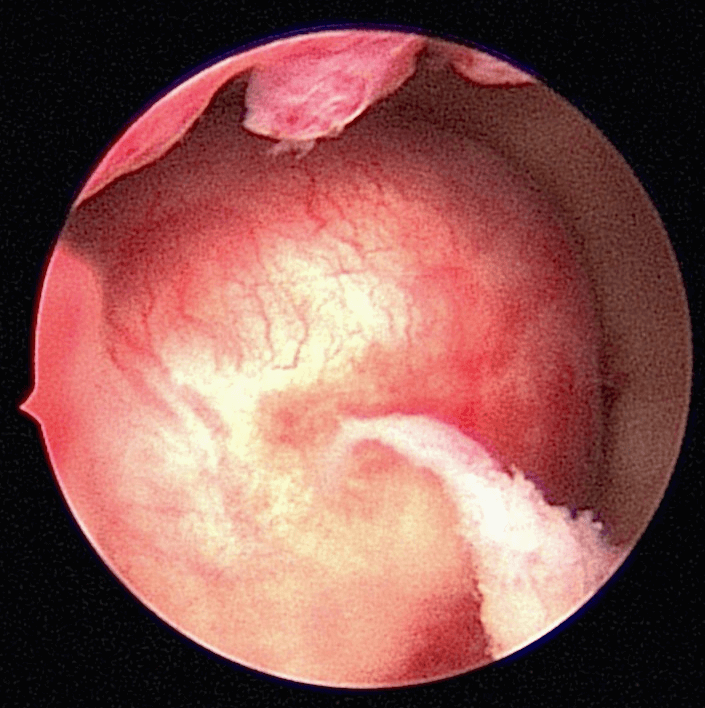
Case 41.1 Spontaneous pregnancy after Transcervical Resection of Fibroid for submucous fibroid
Madam CSB a 37 year old lady with 2 children was referred to me in August 2013 for a problem of inability to conceive for 2 years. Her last child was 5 years of age. She had had 1 episode of heavy menses and dysmenorrhea. Transvaginal ultrasound showed a submucous fibroid measuring 2.71 x 3.25 cm. An Office Hysteroscopy was performed and a large type 2 posterior submucous fibroid was seen (Figure 41.5). Her haemoglobin was only 5.8g%. She was admitted for blood transfusion and was given monthly gonadotrophin releasing hormone analogue (GnRH analogue). She received 3 doses on GnRH analogue. The fibroid reduced in size to 2.19 x 3.04 cm. She underwent a transcervical resection of the fibroid in October 2013. Postoperatively she was well. She spontaneously conceived in June 2014. At the time of writing she was 36 weeks pregnant. (see Video 41.1)
Preoperative Considerations
1) The size of the submucous fibroid is important in deciding the type of surgery. Patients with large submucous fibroids (> 3cm) may need to receive GnRH (g) analogue (gonadotrophin releasing hormone analogue) injections to shrink it. GnRH analogue may be given for 2 – 3 months. It is easier to perform hysteroscopic surgery on a smaller submucous fibroid.
2) The type of fibroid is also important. Generally, type 0 fibroids can be removed easily via hysteroscopy. Type 2 fibroids are more difficult and may require 2 surgeries to completely remove them.
Preoperative preparation
1) The surgery is usually done just after menses. Patients who have received GnRH analogue may not have their menses.
2) The patient will usually be admitted on the same day of the operation. A tablet called misoprostol may need to be either taken orally or placed in the vagina. This tablet is given to soften the cervix so that it will be easy to dilate the cervix during the surgery.
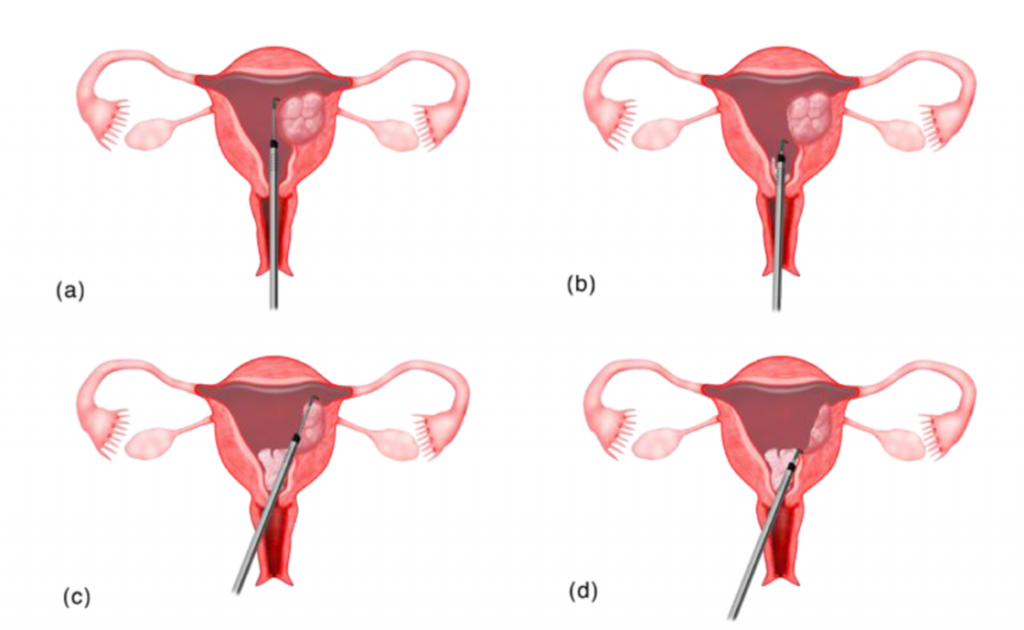
How is the surgery performed?
1) The surgery is usually done under spinal or epidural anaesthesia.
2) The perineum and vagina will be cleaned with antiseptic. Sterile drapes are placed and only the perineum is exposed.
3) The cervix will be dilated to allow passage of a larger diameter hysteroscope (resectoscope).
4) A camera is attached to a hysteroscope so the surgery can be visualised on the monitor.
5) Fluid is used to distend the uterine cavity so that the cavity can be visualised during the surgery.
6) A loop is used and electricity is used to cut the fibroid into small pieces until the base of the fibroid is reached. The small chips of fibroid are then removed through the vagina.
7) Any bleeding seen will be coagulated.

Transcervical Resection of Fibroid
https://vimeo.com/149851760
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mgEwvrRiFpA
The advantages of performing Transcervical Resection of fibroid
1) There is no incision on the abdomen compared to myomectomy by laparoscopy or laparotomy.
2) The patient can conceive immediately after a TCRF as there is no incision in the uterus. After a myomectomy, there will be an incision in the uterus and pregnancy must be deferred for 6- 9 months.
3) Women who are pregnant after TCRF, can have normal vaginal delivery. Women who undergo myomectomy may need to deliver by Caesarean section.
4) Recovery is immediate after TCRF. Myomectomy recovery may take from 1 week (laparoscopic myomectomy)
to 1 month (myomectomy by laparotomy)
Disadvantage of Transcervical Resection of Fibroid
1) Only submucous fibroids can be removed by the TCRF. In myomectomy by laparoscopy or laparotomy, all other fibroids such as intramural or subserous can be removed at the same time.
2) Sometimes, larger submucous fibroids can only be removed with more than one surgery.
Postoperative advice
1) The patient is usually returned to the ward after surgery.
2) If spinal or epidural anaesthesia is given, the patient will experience numbness and weakness of the lower limbs for about 6 hours
3) Some patients may be kept overnight while others may return home the same day.
4) Some women may experience cramping, similar to period pain, after the procedure. There may be shoulder pain, which is caused by the fluid that is used to inflate the uterus. This pain will subside in a few days.
5) There may be some bleeding after the procedure. Bleeding usually subsides in a few days, too.
6) Sexual intercourse must be avoided till bleeding and vaginal discharge stop.
7) Antibiotics may be given before and after the procedure.
8) Tampons should be avoided for at least a month after the hysteroscopy, to help reduce the risk of infection.
9) Severe lower abdominal pain, pain during urination, fever, vaginal discharge that is smelly or unpleasant and heavy bleeding are symptoms that will require the immediate attention of a doctor.
Summary
Transcervical Resection of Fibroid is a good operation for patients with submucous fibroids. There are many advantages of performing TCRF for women with submucous fibroids compared to myomectomy by laparoscopy or laparotomy. TCRF must be performed by a skilled/experienced gynaecologist.
